What is NMN
What is NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) ?
- NMN is a component that assists in keeping youngness and anti-aging. It is a cofactor which originally exists in our cells, but as the body ages, it loses the power to reproduce itself and the NMN levels drop, and due to that, it cannot stop the aging process naturally. However, if we can increase the amount of NMN, we can consider reviving our organs, thus making our life-span longer… Now NMN is becoming known all over the world because it has the highest possibility to control our aging, using today’s science.
※For the first time in the world! We have discovered that the anti-aging cofactor NMN can be used for human bodies safely.
https://www.keio.ac.jp/ja/press-releases/files/2020/1/21/200121-1.pdf 
The Effect of NMN
- “Sirtuin Genes” are sometimes called “Anti Aging Genes” or “Longevity Genes”. Scientists discovered that activating the genes is related to anti aging. The cofactor (NAD), which is produced from NMN in our body, has an important role in this activation, and taking NMN is actually critical in activating the “Sirtuin Genes”.
※Public Interest Incorporated Association, The Japanese Biochemical Society Biochemistry
From ”The possibility as the role of NAD+ synthesis and drug target in Aging Related Disease.
https://seikagaku.jbsoc.or.jp/10.14952/SEIKAGAKU.2015.870239/data/index.html 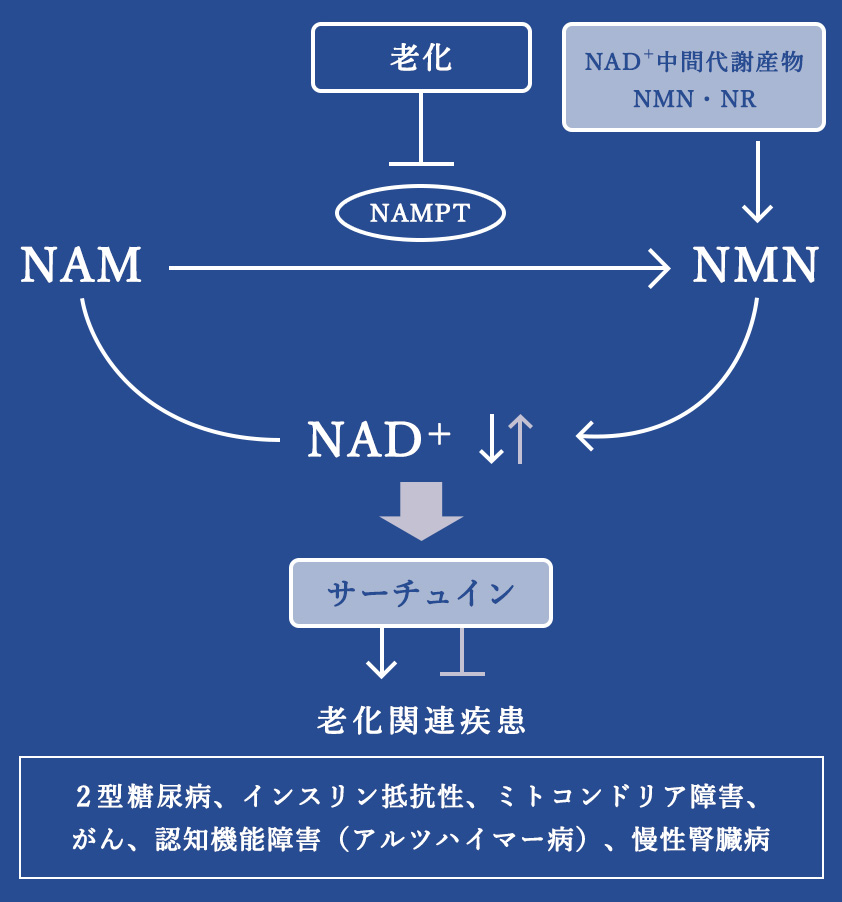
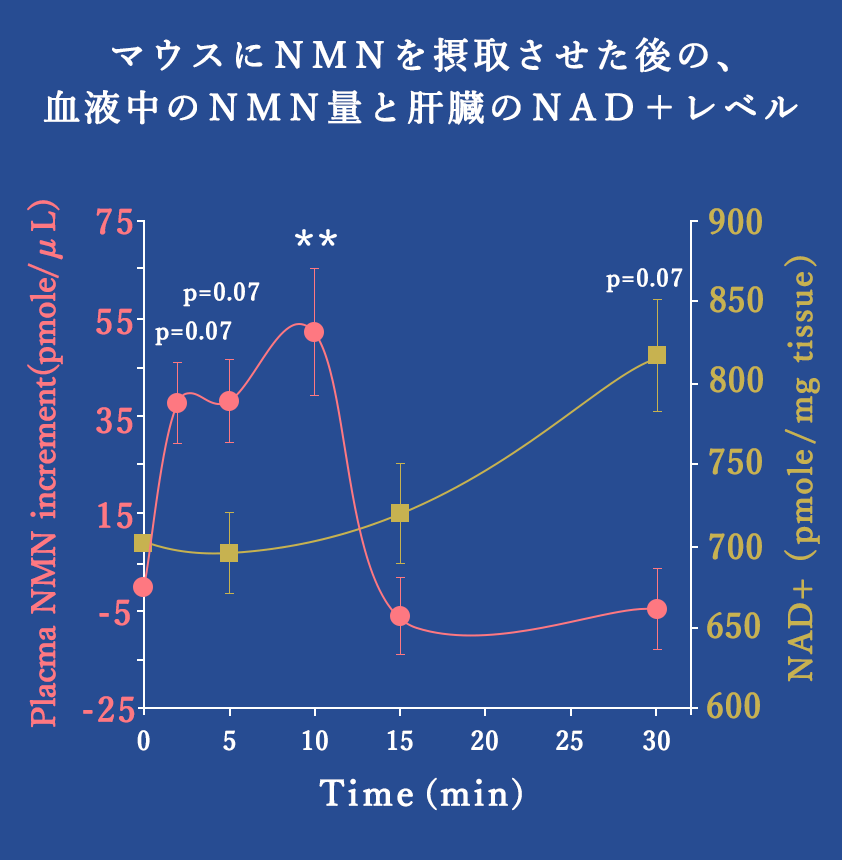
NMN Increases the level of NAD quickly.
- Even if we take the cofactor (NAD) itself, our body does not absorb it. So, taking NMN is the best way to increase the number of NAD in our body. After taking NMN, it will be absorbed in the blood circulation within 5 – 10 minutes, and it will be transported to important organs such as the liver, muscles and brain. Scientists discovered that the level of NAD increased soon after that, when tested on mice.
※「Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice」
Volume 24, ISSUE 6, P795-806, December 13, 2016